What You Will Learn in This Article
- Involuntary incontinence (symptoms, reasons, solutions)
- Vaginal infections: BV, candida, UTIs(symptoms, reasons, solutions)
- Fibroids, uterine polyps, and PMS (pain and bloating) (symptoms, reasons, solutions)
- Vaginal Atrophy: Thinning, pain, sensitive, burning sensation “down there” (symptoms, reasons, solutions)
Involuntary Incontinence
Involuntary incontinence, or the unintentional loss of urine, is a common issue many women face during perimenopause and early menopause. It can affect daily life significantly, but understanding its causes and management strategies can help mitigate its impact. This was one of my first symptoms when I entered perimenopause.
Symptoms of Involuntary Incontinence
Women experiencing involuntary incontinence may notice:
- Urine leakage when sneezing, exercising, or laughing
- An uncontrollable need to urinate
- Sudden leakage without warning
- Discomfort or pressure in the lower abdomen
Why Involuntary Incontinence Happens
Perimenopause and Menopause
During these stages, decreased levels of DHEA, testosterone, and estrogen can weaken the urethral lining and pelvic floor muscles. Additionally, thinning vaginal and urethral tissues provide less support for the bladder.
Pelvic Floor Muscle Weakness
Natural aging and lack of physical activity contribute to the weakening of muscles that support the bladder.
Hysterectomy
The removal of the uterus can affect pelvic floor muscles and nerves, leading to incontinence.
Pregnancy and Childbirth
The pressure of pregnancy and the process of vaginal delivery can weaken pelvic floor muscles and damage nerves that control the bladder.
Chronic Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Frequent UTIs can irritate the bladder, causing sudden urges to urinate.
Other Causes
Conditions such as obesity, chronic coughing, neurological disorders (e.g. MS, Parkinson’s), and certain medications (e.g., diuretics, sedatives) can also contribute to incontinence.
What You Can Do
Strengthen the Pelvic Floor
Improving muscle tone and blood flow can significantly help. Using tools like the Coochball, which involves sitting on the ball for three minutes daily, can release fascia, bring blood flow to the muscles “down there”, and enhance muscle tone. Although Kegel exercises can be beneficial, they are often done incorrectly, leading to mixed results.
Raise Local Tissue DHEA Levels
Products like Julva, a DHEA cream, can locally increase DHEA levels, strengthening the muscles and tissues in the vulva area.
Increase Estrogen Levels
Phytoestrogens found in products like Wise Women’s Balance or Estrogen Boost, and herbs like a red clover tea, black cohosh, dong quai tinctures, or Siberian rhubarb extract can help. For bioidentical estrogen, consulting a functional hormone specialist is recommended.
Consult a Doctor for Other Conditions
For issues related to obesity, chronic coughing, and neurological conditions, seek professional medical advice.
It’s not a sentence – you can change things
Involuntary incontinence can be a challenging condition, but with the right knowledge and tools, it can be managed effectively. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and appropriate interventions can significantly improve the quality of life for women experiencing this condition.
Vaginal Infections: BV, Candida, and UTIs
Vaginal infections can come as a surprise to women in perimenopause given that no significant changes were made – same partner, same diet, same laundry detergent. Bacterial Vaginosis (BV), vaginal candida (yeast infection), and urinary tract infections (UTIs) each have distinct symptoms, causes, and treatments. Understanding these infections is essential for effective management and prevention.
Symptoms of Vaginal Infections
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
- Abnormal vaginal discharge, thin and grayish-white
- Strong fishy smell, especially noticeable after intercourse
- Vaginal itching and irritation
- Burning sensation
- Mild pain during intercourse
Vaginal Candida (Yeast Infection)
- Intense itching and irritation in and around the vaginal area
- Cottage cheese-like discharge, usually odorless
- Redness, swelling, and soreness
- Burning, especially during urination or sexual intercourse
- Discomfort during sexual activity
- Rash and vaginal dryness (less common)
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Painful and burning urination
- Cloudy and strong-smelling urine
- Blood in urine
Causes of Vaginal Infections
Imbalance of Vaginal Bacteria
BV: Overgrowth of harmful bacteria like Gardnerella vaginalis and insufficient Lactobacilli disrupt the vaginal environment.
UTIs: Overgrowth of Escherichia coli (E. coli) often due to frequent antibiotic use.
Diet: Processed Carbohydrates & Sugar
High intake of alcohol, sugar, processed carbs, coffee, and inflammatory foods alters digestive bacteria, impacting vaginal health.
Decreased DHEA/Estrogen Levels
Lower estrogen levels decrease glycogen production, reducing Lactobacilli activity and increasing vaginal pH. Thinning vaginal walls become more prone to irritation and infection.
Sexual Activity
Multiple or new sexual partners can increase infection risk.
Douching
Frequent douching disrupts the natural balance of vaginal bacteria.
Urinary Retention
Incomplete bladder emptying or holding urine for long periods promotes bacterial growth, leading to UTIs.
Management and Prevention
Correct Bacterial Balance
- Use probiotics with Lactobacilli strains (L. crispatus, L. jensenii, L. gasseri) like She-Biotics.
- Avoid antibiotics when possible.
- Reduce sugar, alcohol, and coffee intake.
Raise DHEA and Estrogen Levels
- Apply Julva DHEA vaginal cream to correct local DHEA levels.
- Use phytoestrogen supplements like Wise Women’s Balance or Estrogen Boost.
- Consider herbal remedies like red clover tea, black cohosh, dong quai tinctures, or Siberian rhubarb extract.
- Consult a functional hormone specialist for bioidentical DHEA or estrogen treatments.
Conclusion
Vaginal infections in perimenopause and menopause such as BV, candida, and UTIs are common but manageable with the right knowledge and tools – which may include hormonal correction. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and effective interventions, women can take proactive steps to maintain their vaginal health and overall well-being.
Fibroids, Uterine Polyps, and PMS: Symptoms, Causes, and Management
Fibroids, uterine polyps, and premenstrual syndrome (PMS) are common conditions affecting many women, particularly during perimenopause when our hormones fluctuate a great deal. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the underlying causes can help in managing these conditions effectively.
Symptoms
Fibroids (Leiomyomas or Myomas)
- Heavy menstrual bleeding and prolonged periods
- Passing large blood clots during menstruation
- Pelvic pain and pressure, lower back pain
- Frequent urination and difficulty emptying the bladder
- Visible swelling or enlargement of the lower abdomen
- Pressure on the rectum leading to constipation
- Discomfort during sexual intercourse
- Infertility or difficulty getting pregnant
Uterine Polyps
- Irregular or unpredictable menstrual cycles
- Heavy menstrual periods
- Spotting or bleeding between periods and after menopause
- Difficulty conceiving or carrying a pregnancy to term
- Pelvic pain
PMS Symptoms
Physical: Bloating, breast tenderness, headaches, fatigue, weight gain, joint or muscle pain, acne, digestive issues, food cravings, swelling in hands or feet.
Emotional and Behavioral: Mood swings, irritability, anxiety, depression, crying spells, difficulty concentrating, changes in sleep patterns, appetite changes, decreased interest in activities, social withdrawal.
Why It’s Happening
Hormonal Changes
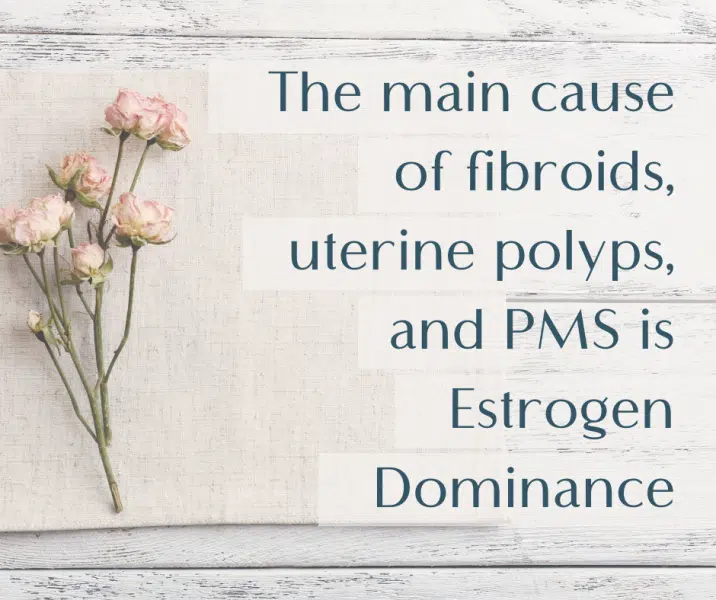
Estrogen Dominance: The main cause of fibroids, uterine polyps, and PMS is a hormonal imbalance where estrogen levels are high relative to progesterone.
Low Progesterone Levels: Often due to insufficient progesterone rather than excessively high estrogen, especially common in perimenopause.
Dietary Choices
- Diets high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can exacerbate hormonal imbalances.
- Alcohol can increase estrogen levels.
Obesity and Belly Fat
Adipose tissue produces estrogen, contributing to estrogen dominance.
Environmental/External Estrogens (Xenoestrogens)
Chemicals in plastics (BPA), pesticides, and personal care products mimic estrogen and disrupt hormonal balance.
Impaired Liver Detoxification
The liver metabolizes and detoxifies estrogen; dysfunction can reduce the ability to process and eliminate “dirty” estrogens.
Other Hormonal Imbalances
Chronic stress and hypothyroidism can disrupt the balance of estrogen and progesterone.
What You Can Do
Immediate Relief
Use the EaseAway Uterine Cream to lessen inflammation and reduce discomfort using herbs beneficial for reproductive organs.
Address Estrogen Dominance
- Start with the book “Overcoming Estrogen Dominance” for diet and lifestyle changes, supplements, and herbs to help.
- Balance estrogen levels with Wise Women’s Balance or Estrogen Boost.
- Reduce consumption of coffee, sugar, and alcohol.
- Replace synthetic perfumes and mainstream skincare products with clean, organic brands.
Conclusion
Managing fibroids, uterine polyps, and PMS involves understanding the symptoms and addressing the underlying causes, primarily estrogen dominance. By making informed dietary choices, managing stress, and using appropriate supplements and herbs, women can improve their health and alleviate symptoms. For persistent issues, consult with a healthcare professional.
Vaginal Atrophy: Symptoms, Causes, and Management
Vaginal atrophy is a common condition among women, particularly in menopause, characterized by the thinning of vaginal walls and a range of discomforts. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the underlying causes can help manage this condition effectively.
Symptoms of Vaginal Atrophy
- Thinning of vaginal walls
- Vaginal dryness and lack of natural lubrication
- Burning sensation in the vagina or during urination
- Pain during intercourse
- Vaginal itching and irritation
- Increased sensitivity to soaps, detergents, or latex
- Possible swelling or rash in the affected area
Why It’s Happening
- Decreased DHEA Levels: Lower DHEA levels cause thinning and weakening of vaginal walls.
- Decreased Estrogen Levels: Post-menopause, reduced estrogen leads to thinner vaginal walls and bacterial imbalance.
- Bacterial Balance: Lower estrogen can disrupt the balance, promoting pathogenic bacteria.
- Lack of Blood Flow: Reduced blood flow to the pelvic floor muscles exacerbates atrophy.
What You Can Do
Raise DHEA Levels
- Julva Cream: The Julva cream (formulated by Dr Anna Cabeca) popular choice within the community for local application in the vaginal area.
- Systemic DHEA: Consult a functional hormone specialist for bioidentical DHEA prescriptions.
Raise Estrogen Levels
- Herbal Options: Wise Women’s Balance or Estrogen Boost, red clover tea, black cohosh, dong quai tinctures, or Siberian rhubarb extract.
- Bioidentical Estrogen: Work with a functional hormone specialist for personalized treatment.
Balance Vaginal Microbiome
- Diet Adjustments: Avoid sugar, alcohol, and processed foods.
- Probiotics: Introduce Lactobacilli strains (L. crispatus, L. jensenii, L. gasseri) through products like She-Biotics.
Restore the Pelvic Floor and Muscles
- Coochball: The Coochball has been a game-changer for many women (including for me, Magdalena). Use it for 2-3 minutes daily to activate fascia and improve blood flow.
- Kegels: Can be helpful but results vary; consider guidance on proper technique.
Conclusion
Managing vaginal atrophy involves addressing hormonal imbalances and improving vaginal health through lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and targeted treatments. If you experience symptoms of vaginal atrophy, consult with a healthcare professional to explore the best treatment options for you.






Thank you for providing such a simple yet important information about women’s bodies! With new health care restrictions happening all over the country we are going backwards in time and information is being kept from us instead of moving us forward.